Cathodic protection package series
Home > Products > Cathodic protection package series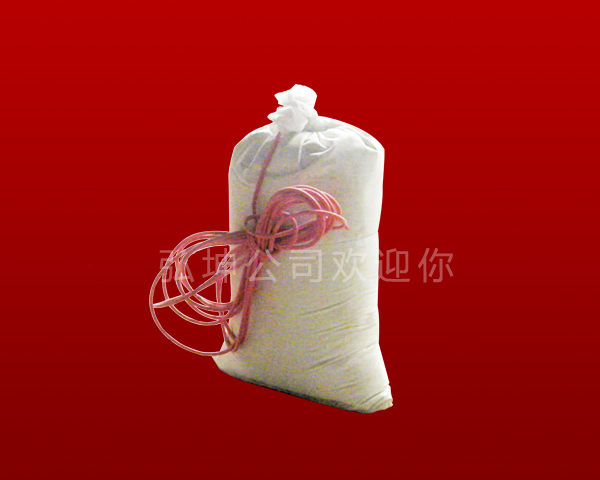
Zinc reference electrode Uses: 1. Precise monitoring of cathodic protection status. Used as a sacrificial anode protection potential measurement, protection potential between 0V ~ + 0.25V.
2. In the external current cathodic protection system, for the automatic control of the stable signal source. Applicable to buried pipes and underground metal structures cathodic protection works.
3. Can be buried in the need to monitor and can not enter the location, such as: the bottom of the location of large containers, underground fuel storage, chemical tank can not be close to the location between the city road under the pipe network, etc., during the construction period in advance Buried, long-term use. 4. Telemetry source for pipeline cathodic protection.
I. Introduction
The reference electrode is one of the important components of the cathodic protection system. It can be used to measure the potential of the protected structure, but also as a potentiometer automatically control the source. Commonly used buried long-life reference electrode with Cu / CuSO4 reference electrode and zinc reference electrode, zinc reference electrode due to its compression characteristics, in some ceramic cans of copper sulfate reference can not be used to show its advantages The But at the same time zinc electrode potential stability than copper sulfate reference electrode is good, it is recommended that the two use.
Second, the installation guide
1. Buried position: the electrode is usually buried in the protection of metal structures near the ground is deep enough (usually 1 meter or so) of the soil, in a permanent moist environment. In areas where the groundwater level is high, the electrodes are buried in soils above 20 cm above the groundwater level, and the permafrost regions should be buried below the permafrost.
2. Buried method:
1) Immerse the reference electrode in an appropriate amount of distilled water or clean fresh water for not less than 2 hours.
2) Buried packing bags with electrodes buried in the buried pits are pre-dug and the surrounding soil is compacted, and then the appropriate amount of fresh water is poured into the buried sites to improve the electrode connection state.
3) Connect the electrode lead to the measuring circuit.
Third, pay attention to matters
1, the electrode handling should be careful to avoid, so as not to break, shock crack electrode, not allowed to pull the cable for handling tools.
2, the electrode should be placed in the buried before the dry and dry place, to avoid sun sun and rain.
3, to avoid with other chemicals together.
4, in the entire handling and installation process, to prevent the break through the cable insulation.
| Material | model | shape | life | Applicable environment |
| Zinc electrode | CX-I | Cylindrical | >6 | High purity zinc, used in seawater, light sea water |
| CX-II | Cylindrical | >6 | Zinc alloy for seawater, light sea water |
The main technical indexes of high purity zinc reference electrode
| Critical current density | +38--10uA/cm2 |
| Potential accuracy | ≤±60mV |
| Electrode design life | According to the requirements of design |
| Open circuit potential | -940mV(vs,SHE) |
 Magnesium alloy sacrificial anode
Magnesium alloy sacrificial anode Zinc alloy sacrificial anode
Zinc alloy sacrificial anode Aluminum alloy sacrificial anode
Aluminum alloy sacrificial anode Magnesium ribbon
Magnesium ribbon  Zinc belt
Zinc belt constant potential rectifier
constant potential rectifier Deep well anodes
Deep well anodes High silicon cast iron anodes
High silicon cast iron anodes Flexible anode
Flexible anode MMO anode
MMO anode Cathodic protection of copper welding machine
Cathodic protection of copper welding machine Ground Resistance Tester
Ground Resistance Tester Zinc grounded battery
Zinc grounded battery Zinc reference electrode
Zinc reference electrode Fill in the package material
Fill in the package material Aluminum heat flux
Aluminum heat flux Explosion-proof junction box
Explosion-proof junction box Test piles
Test piles Long - acting copper sulfate reference electrode
Long - acting copper sulfate reference electrode Silver / silver chloride reference electrode
Silver / silver chloride reference electrode Cathode protection cable
Cathode protection cable Heat shrinkable tape
Heat shrinkable tape Aluminum heat welding mold
Aluminum heat welding mold Insulation bracket
Insulation bracket Insulated joints
Insulated joints Insulated flange
Insulated flange Polarization Probe
Polarization Probe Anticorrosion tape
Anticorrosion tape Point guns
Point guns Injury tablets
Injury tablets Logo pile
Logo pile Portable reference electrode
Portable reference electrode